The Silent Sentinels: Using LLMs to Detect Emerging Risks in Your Company's Communications
How LLMs Turn Organizational Chats into Early Risk Warnings
Kas is a banker turned technocrat. Obsessed with Banking, Regulatory Technology, AI, and the mess in between. Reach me on LinkedIn.
Introduction
In today's fast-paced business world, risks can emerge from unexpected corners, often hidden within the everyday communications of an organization.
Detecting these "weak signals" before they escalate into full-blown incidents is the holy grail of enterprise risk management (ERM). This is where the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) comes into play, transforming how businesses proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats.
LLMs offer a revolutionary capability: monitoring communications for signs of emerging risks. This isn't just about spotting obvious red flags; it's about uncovering subtle linguistic cues and patterns that hint at potential problems long before they manifest as tangible incidents.
Imagine having an early warning system that constantly sifts through your organization's digital pulse, flagging concerns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
What Does This Involve? The Data Landscape
At its core, this powerful application of LLMs involves analyzing vast amounts of unstructured text data generated within an organization. These internal communication sources provide a rich, real-time tapestry of your company's operational health and potential vulnerabilities.
Typical internal communication sources monitored include:
Emails: A treasure trove of formal and informal communication, often containing early discussions about issues, concerns, or policy interpretations.
Chat platforms (e.g., Microsoft Teams, Slack): Real-time, often less formal discussions where frustrations, workarounds, or unspoken concerns might first surface.
Meeting transcripts: Recordings of formal and informal discussions that can reveal evolving strategies, new challenges, or disagreements.
Customer service calls/tickets: Direct feedback from customers, which can highlight recurring product flaws, service gaps, or emerging dissatisfaction trends.
Audit and inspection reports: Formal documents detailing compliance, operational efficiency, and control effectiveness, which can indicate areas of weakness.
Board or management meeting minutes: High-level discussions about strategic risks, market changes, and internal challenges.
By tapping into these diverse data streams, organizations gain a comprehensive view of their internal landscape, enabling LLMs to detect nuanced risk signals.
How LLMs Can Help: Uncovering the Unseen
Emerging risks are inherently elusive. They are new or evolving threats that haven't yet been fully understood, formally documented, or even widely recognized. They're the nascent whispers of a problem before it becomes a shouting match.
Examples of emerging risks that LLMs can help detect include:
Early signs of employee misconduct: Subtle hints of unethical behavior, policy violations, or conflicts of interest.
Repeated complaints about a vendor or tool: A consistent pattern of dissatisfaction that could indicate operational disruptions or financial implications.
Increasing chatter around process gaps or fraud suspicion: Informal discussions among employees that highlight loopholes, workarounds, or concerns about suspicious activities.
Whistleblowing: Anonymous mails/chats leading to a larger issue such as fraud or harassment
Regulatory gray areas that teams are unsure about: Employees discussing confusion or uncertainty regarding new regulations, potentially leading to non-compliance.
LLMs, with their advanced natural language processing capabilities, are uniquely equipped to sift through this unstructured text and identify these subtle cues.
They can:
Identify risk-related themes and tone shifts: Detecting when conversations shift towards negativity, concern, or a focus on problems.
Uncover unusual patterns or repeated concerns: Spotting recurring keywords, phrases, or topics that indicate a persistent underlying issue.
Analyze sentiment changes around specific issues: Tracking how the general mood or feeling towards a particular project, policy, or client evolves.
Detect mentions of control failures or violations: Identifying explicit or implicit references to bypasses, breakdowns in processes, or non-compliance.
Consider these common patterns and their inferred risks:
“We’ve flagged this several times, but still no fix”: Operational negligence
“The client is threatening escalation.: Reputational/Compliance
“This bypass works, but let’s keep it between us”: Control circumvention
“We had to disable the firewall temporarily”: Cyber/IT risk
“I’m not sure if this violates policy”: Compliance ambiguity
LLMs can be specifically prompted or fine-tuned to recognize and flag such linguistic cues, acting as intelligent risk sensors.
Workflow: From Monitoring to Action
Implementing an LLM-powered emerging risk detection system involves a structured workflow, transforming raw communication data into actionable intelligence.
Step 1: Ingest and Normalize Data
The first step involves collecting data from various communication channels. This data is then cleaned and normalized to ensure consistency. Crucially, anonymization is a critical consideration at this stage to address data privacy and compliance requirements.
Step 2: Risk Signal Detection (LLM Prompt Examples)
This is where the LLM's analytical power comes into play. Prompts are designed to guide the LLM in identifying implicit risks and assessing their severity.
Example Prompt:
"Based on this message, identify any implicit risks and rate their severity: 'Can we settle this off the books for now? Accounting will get messy otherwise."
LLM Response:
Risk Detected: Financial misreporting
Severity: High
Category: Compliance / Financial Integrity
Step 3: Summarize & Cluster
Once individual messages are analyzed, the LLM can then be used to aggregate and organize the detected risks. This involves:
Summarizing frequently mentioned risks: Identifying the most common risk themes across the data.
Clustering messages by risk themes: Grouping similar risk-related messages for easier analysis.
Tracking how often a risk theme recurs: Monitoring the frequency of specific risk mentions over time to identify trending concerns.
Step 4: Alerting & Visualization
The final stage involves translating the LLM's insights into actionable alerts and easy-to-understand visualizations for risk and compliance teams.
High-risk messages routed to the compliance team: Immediate notification for critical findings.
Volume of risk mentioned by theme shown in dashboards: Providing a high-level overview of emerging risk areas.
Emerging risk heatmaps generated monthly/weekly: Visualizing the severity and frequency of different risk types over time.
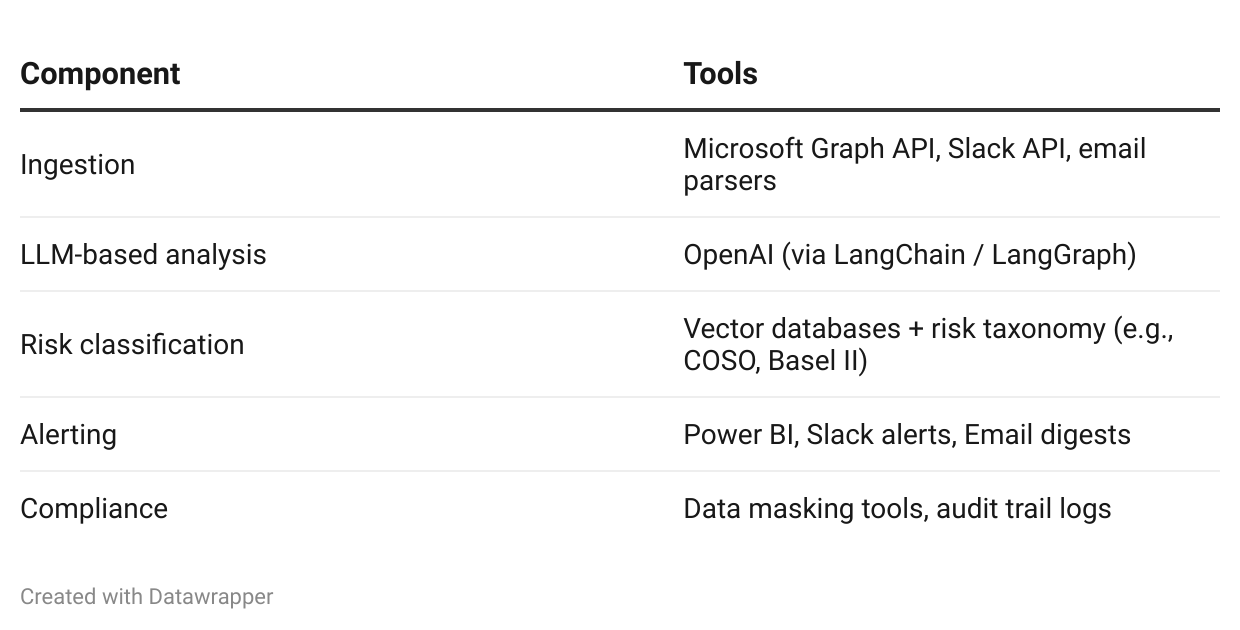
Tooling Setup: The Technology Stack
Implementing such a system requires a combination of robust tools and technologies.
This integrated stack ensures seamless data flow, powerful analysis, and effective dissemination of risk intelligence.
Sample Output: A Glimpse into Risk Intelligence
A monthly digest of emerging risk signals provides a concise yet comprehensive overview for risk and compliance teams.
Emerging Risk Signals – June 2025
Increase in control circumvention messages from front-office teams (28 instances, up 40%) - This indicates a potential weakening of internal controls and necessitates an immediate review.
Cybersecurity concern flagged in 12 emails mentioning “firewall” or “patch delay” - Highlights potential vulnerabilities in IT infrastructure that require attention.
Client dissatisfaction trend noticed from 3 departments (sentiment drop detected) - Signals potential reputational risk and a need to investigate customer experience issues.
Shortcuts in Reconciliation (Finance Team) - Indicates a potential process inefficiency or compliance risk within financial operations.
Benefits to Risk/Compliance Teams: A Paradigm Shift
The advantages of leveraging LLMs for emerging risk detection are profound, shifting ERM from a reactive to a proactive discipline.
Early warning system based on behavioral cues: Moving beyond formal reporting to detect risks based on how employees communicate.
Identification of non-reported risks: Uncovering issues that might not be formally escalated through traditional channels.
Prevents issues from escalating (e.g., Wells Fargo sales practice scandal): By detecting early signals, organizations can intervene before minor issues explode into major crises.
Continuous risk intelligence, rather than point-in-time audits: Providing an ongoing, dynamic view of the risk landscape, rather than relying on periodic assessments.
Challenges: Navigating the Hurdles
While the benefits are significant, implementing such a system comes with its own set of challenges that need careful consideration.
Data privacy and surveillance concerns: This is paramount. Robust policies, explicit consent, and advanced data masking techniques are essential to protect employee privacy. Transparency about the monitoring process is crucial.
False positives: LLMs, while powerful, can sometimes misinterpret context, leading to false alarms. This requires continuous model tuning and a human-in-the-loop validation process to verify flagged risks.
Regulatory scrutiny: The use of AI in risk management is an evolving area of regulation. Organizations need to ensure clear audit trails for AI-based risk decisions to demonstrate compliance and accountability.
Integrate with GRC Systems
The true power of this capability is unleashed when insights from LLMs are integrated with existing Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms (e.g., Archer, MetricStream, LogicGate).
This creates a holistic and interconnected risk management ecosystem, feeding:
Risk registers: Automatically updating lists of identified risks with real-time data from communications.
Control testing alerts: Triggering alerts when communications suggest potential control failures, prompting targeted testing.
Incident logs: Providing valuable context and early warnings for incidents, improving response times, and post-incident analysis.
By embracing LLMs in enterprise risk management, organizations can move beyond traditional, often reactive, approaches to risk.
The organization can cultivate a culture of proactive vigilance, transforming everyday communications into a powerful source of real-time risk intelligence, ultimately safeguarding its operations, reputation, and future.